Depending on the process, different techniques are used
There is a wide variety of types of moulding processes which are ways of manufacturing by shaping liquid or pliable material using a rigid frame called a mould. Depending on the process, different temperatures are used to create the end product.
The most popular techniques are rotational moulding, blow moulding, injection moulding, extrusion moulding, compression moulding, and thermoforming. Rotational moulding is a process for producing large hollow products and parts. This involves putting a powder or liquid resin into a mould and rotating it in an oven. The movement creates force and when the mould cools down, the hardened plastic is removed. Storage tanks and car parts are common end products.
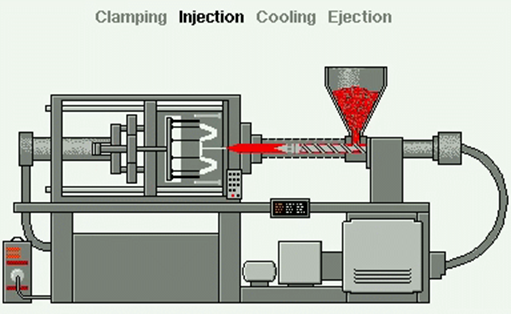
Injection moulding is used for making high volume plastic parts.
Blow moulding is used to create customised plastic parts. The machines heat up the plastic and inject air inside. This then forms a balloon shape. The plastic is blown into a mould and it takes shape. It’s then cooled and hardened. Common items resulting from blow moulding include bottles, oil tanks and plastic drums.
Industry use
Industries which require a silicone moulding service can benefit from precision moulding companies such as http://www.meadex.co.uk/silicone-mouldings.
Common uses for injection moulding include car parts. This process is used for making very high volume plastic parts. These are made by injecting molten plastic material into a metal mould. It’s then cooled and opened.
According to Packaging Gateway Canada-based plastic injection moulding firm The Quality Model Group is set to invest $9.5m to expand its Orangeburg County plastic injection moulding operations in the USA.
Extrusion moulding is a process which is similar to injection moulding, the difference being that a long shape is formed, and instead of a mould, a ‘die’ is used. The parts are created by pushing hot material through a die. The die shape, as opposed to a mould, determines the shape of the end product.
Compression moulding involves a heated plastic material which is placed into a hot mould and then shaped. When the correct shape has formed, the product is cooled, trimmed and removed. The car industry places a strong reliance on compression moulding. The cost of a compression mould is substantial, but the main advantage is that the cost of each part is low when produced at high quantities.